Sentiment Analysis
The study of the noise impacts from aircraft operations at the airport on the social, economic, and health impacts of the population living nearby, particularly the area beneath the major flight paths, is an epidemiological study that involves many techniques to collect data from respondents. Therefore, it is a large-scale project involving multiple disciplines. A self-reporting technique often collects a large amount of data and requires mathematical and statistical processing or the use of mathematical models to process the data, which must work with computer researchers to propose the algorithm or models for data analysis to results that may practically be useful to construct proposal on policies and regulations for managing noise impacts from the international aviation hub.
The Ficture Frustration study (the PF-study) is a self-reporting technique to collect the noise impacts opinion from people living in the vicinity of the airport. The large amount of collected data in textual format needs efficient analytic tools for data analysis and interpretation of the results. Sentiment analysis is a common use of Large Language Models (LLMs) that utilize advanced artificial intelligence (AI) systems to determine textual data and comprehend the opinions conveyed within it. This technique is therefore very useful for analyzing textual data and for assessing the perceptions of the respondent to be used in assessing self-reported health impacts in line with the epidemiological approach.
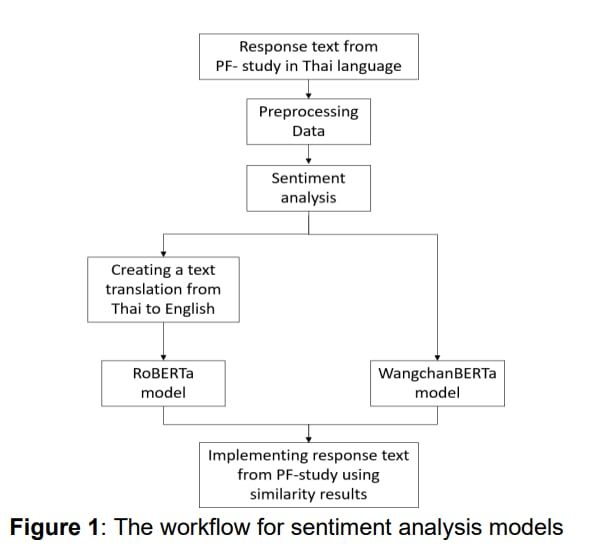
An initial sentiment analysis using the pre-trained models, RoBERTa and WangchanBERTa models, was proposed to perform the firsthand analysis using the dataset from the PF-study around Suvarnabhumi Airport. (Figure 1) For more details, please read the conference research paper in the proceedings of the ICBEN 2023 at https://icben2023.com/papers.
An illustration of a questionnaire form used in the PF study, which was first created and applied in a Japanese study on the effects of airport noise on daily life convenience. Similar studies in Thailand and Vietnam continued to use it. To find the best mathematical model to assess the outcomes by analyzing the textual data using automated sentiment models, the research team can test the models they have proposed using the dataset from those studies. The Gold Standard for training and testing under validation of the mathematical models must be found through the implementation of the human annotation procedure during the sentiment model development process. It is the most important step in the model development process that must be completed till the model is more precise. This will make the researchers' work more convenient and efficient in the future.
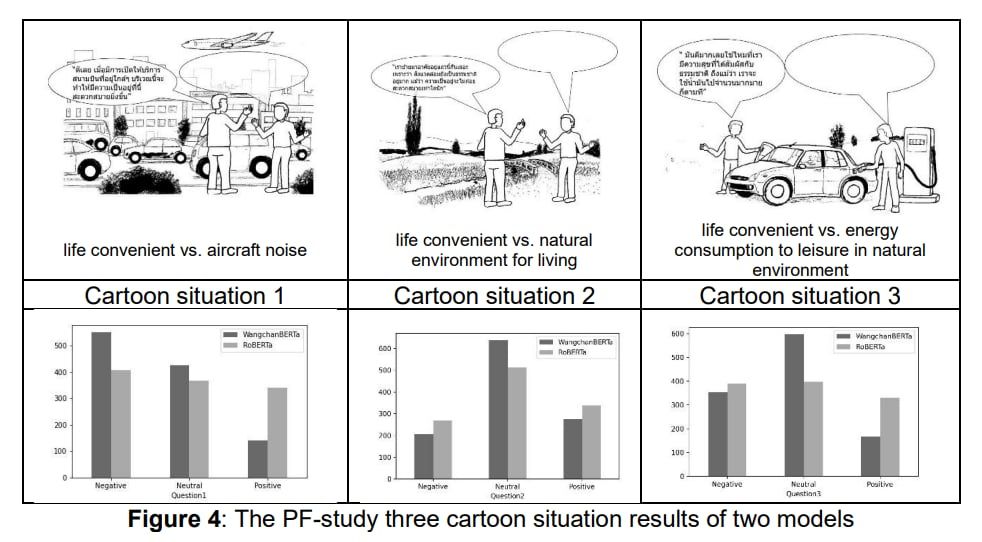
This project is still in progress; in 2024 the research team proposed sentiment analysis using the pre-trained models RoBERTa, WangchanBERTa, and Typhoon models to complete the dataset from the PF-study around Suvarnbhumi Airport with human annotations, making the gold standards for training and testing the models. The results will be presented in the manuscript of IJERPH submitted to the editor this year. This lab member's publications are available for viewing if you're interested.
The further step will do a comparative study of the sentiment models with human annotations in the local language. The research team is now preparing the dataset to train and run models using the same dataset from the PF-study around Suvarnabhumi Airport; the PF-study around Noibai Airport was contributed by a research team from the Osaka Institute of Technology in Japan. This year's research will be conducted in collaboration with international researchers. In many respects, we will most likely learn from each other about the challenges of sentiment analysis in the PF-study data. The further study is still open for young researchers to join this project.